Chapter-1
The Living World
*Points to Remember:-
- 1. Organism (Microorganism, plant and animals) who posseses life is living.
- 2. life is a complex Organism expressing itself through chemical reactions and exhibit characteristics of living organisms.
- 3. Characteristics of Living Organisms: Growth, reproductionn metabolism, cellular organisation, consciousness, self-replicating and self regulation.
- Reproduction and groth are not defining properties.
- Metabolism (Catabolic + Anabolic), cellular organisation and consciousness are defining properties.
- Living organisms are self-replicating, evolving, self-regulating and interactive systemes capable of reponding to external stimuli.
- 4. Biodiversity : The term used to refer to the variety of micoorganism, plant and animals on earth.
- 5. Need for Classification : To organise the vast number of microorganism, plants and animals into categories that could be named, remembered, studied and understood.
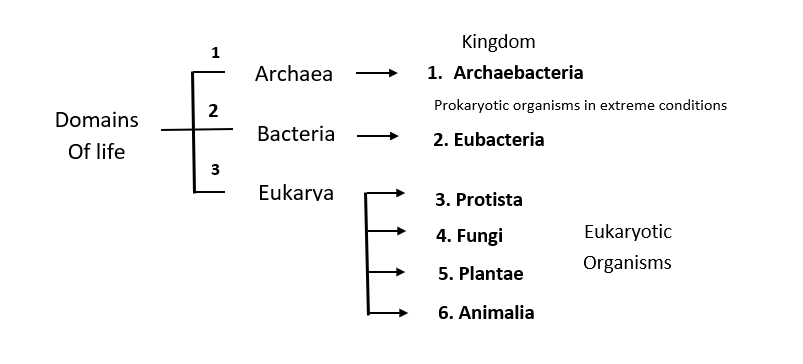
- 6. Three Domains of Life : Proposed by Carl Woese in 1990m who also proposed the six kingdom classification for living organisms. The three Domains of life are Archaea, Bacteria and Eukarya.
- 7. Taxonomy : Study of principles and procedures of indentification, nomenclature and classification.
- 8. Systematics : It deals with classification of organisms based on their diversities and relationships among them. The term was proposed by Carolus Linnaeus who wrote 'Systema Nature'.
- 9. Concept of Species : All the members that can interbreed among themselves and can produce fertile offsprings are the members of same species. This is biological concept of species proposed by Mayr.
- 10. Taxa : Each category (i.e., unit) of classification is called as a taxon.
- 11. Taxonomic Hierarchy : Classification of organisms is a difnite sequence of taxon or category or rank in a desecending order.
Kindgom → Phylum/Division → Class → Order → Family → Genus →Species.
- 12. Binomical Nomenclature : Given by carolus Linnaeus. Each scientific name has two components-Generic name + Specific epithet.
- 13. ICBN : International Code for Botanical Nomenclature (for giving scientific name to plants.)
- 14. ICZN : International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (for giving scientific name to animals.)
15. Rule for Nomenclature :-
- Latinised names are used.
- First word is genus, second word is species name.
- Printed in italics; if handwritten then underlined separately
- First word starts with capital letter while species name written in small letter.
16. Scientific names of some organisms :-
-
Man - Homo Sapiens
Housefly - Musca Domestica
Mango - Mangifera indica
Wheat - Triticum aestivum
-
17. Taxonomical Aids are the tools for study of taxonomy.
- 18. Museums in educational institutes (school and collegs) have collection of skeletons of animals, stuffed and preserved specimens of organisms for study and reference.
- 19. Zoological Parks (Places where wild animals are kept in procted environment under human care) Example : National Zoological Park, Delhi.
- 20. Herbarium : Store house of dried, pressed and preserved plant specimen on sheets, kept systematically according to a widely accepted system of classification, for future use.
- 21. Botanical Garden : Collection of living plants for reference.
Example : Royal Botanical garden Kew (England), National Botanical Research Institute (Lucknow), Indian Botanical Garden (Howrah, Kolkata).
- 22. Keys : (Used for indentification of plants and animals on the basis of similarities and dissimilarities.) two types < Indented key, Bracketed key.
- 23. Couplet : are the two alternate characteristics statement used in key to identify organisation.
- 24. Each Statement of the key is called a lead.
- 25. • Flora (Index to plant species found in a particular area.)
- 26. • Manuals (Provide information for indentification of name of species in an area.) It is a handy book.
- 27. • Monographs (Contain information on any one taxon.)